



Durable and Low-Friction Linear Rails for High-Speed Equipment
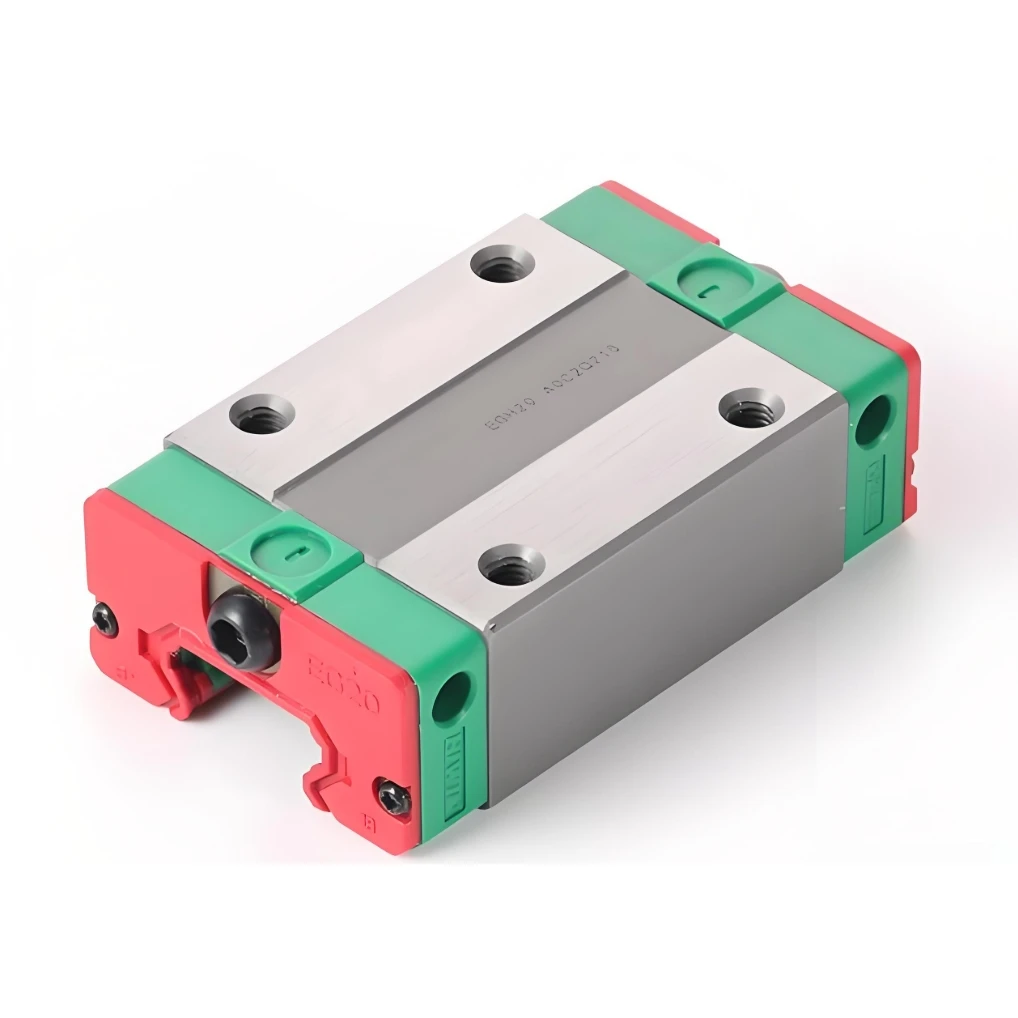
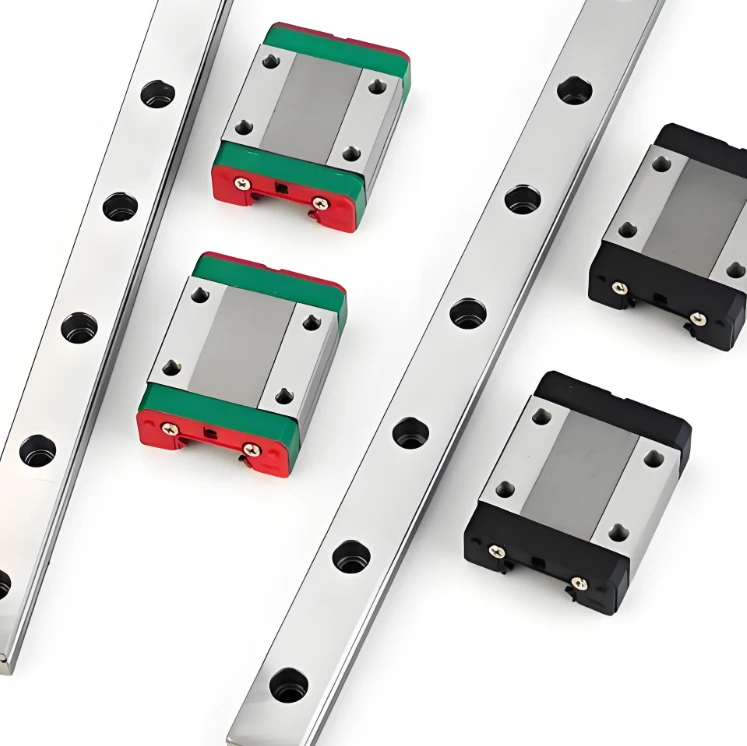
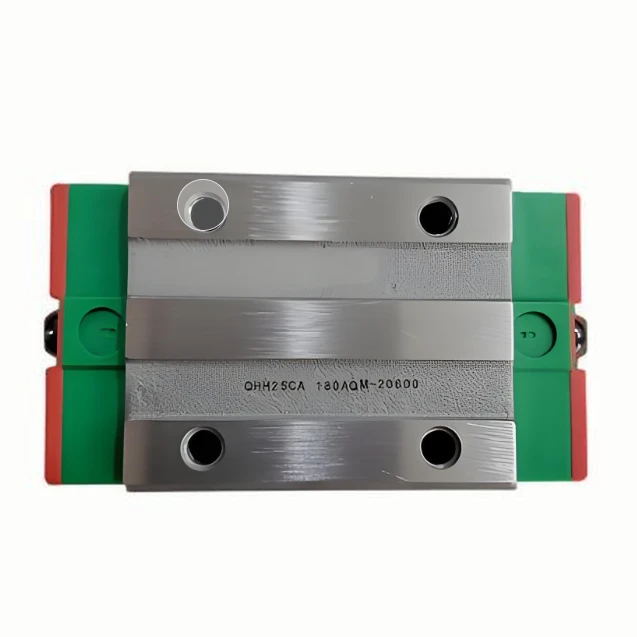
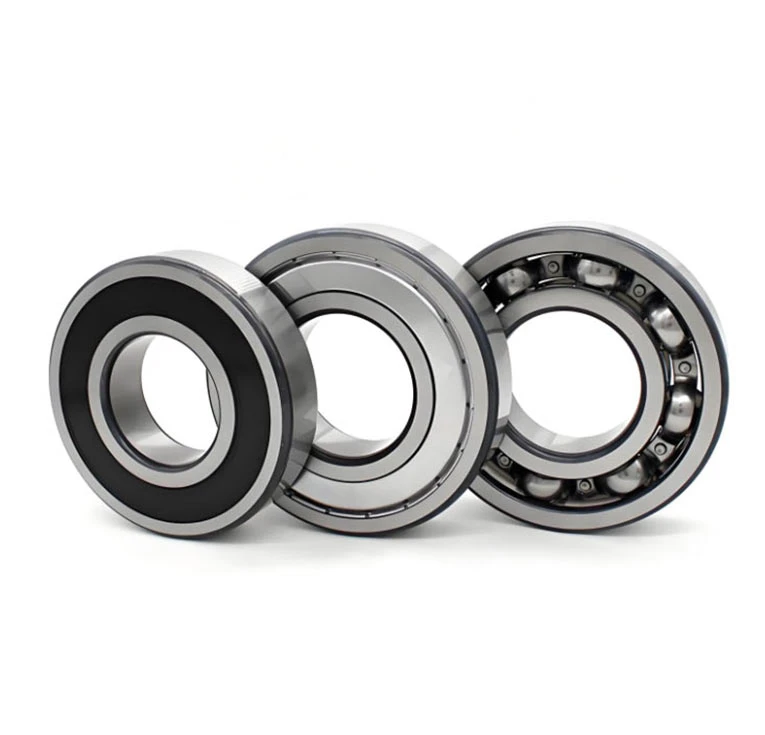
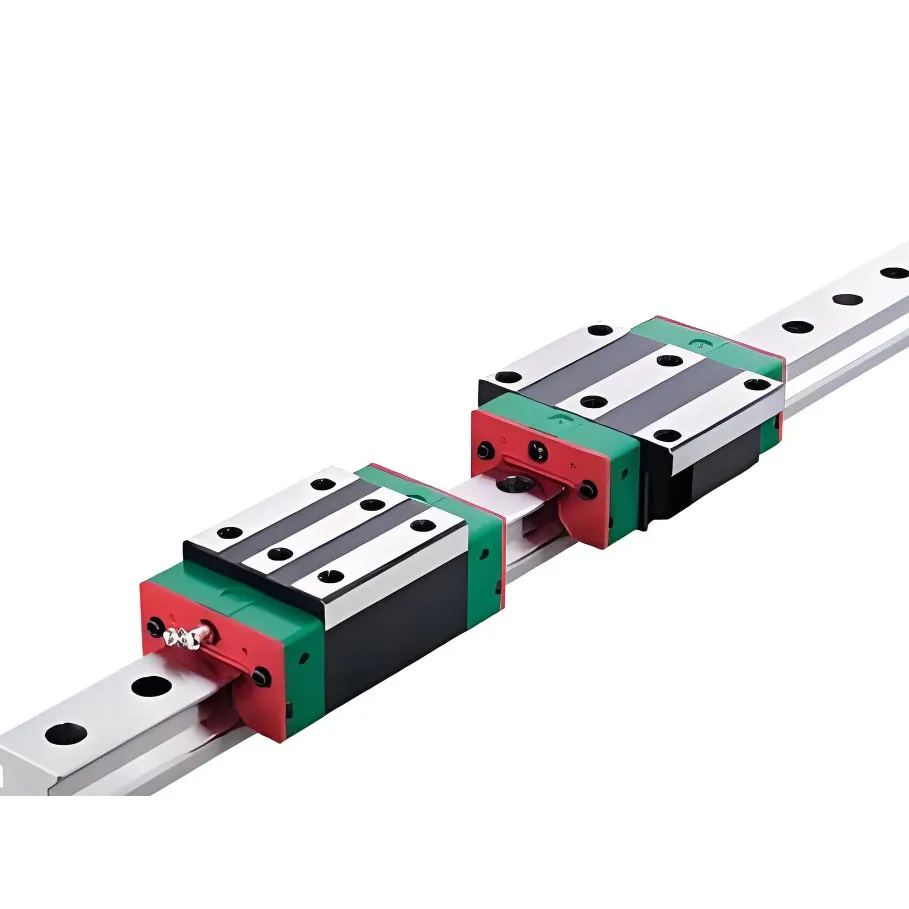
A high precision linear guide, also known as a linear motion guide or linear rail, is a mechanical component designed to support and guide motion in a straight line with high accuracy and low friction. It typically consists of a rail and a carriage (or block) that moves along the rail with the help of ball bearing linear guide mechanisms, such as recirculating ball or roller bearings. These guides are widely applied in CNC machines, 3D printers, automation systems, packaging machinery, and other industrial equipment requiring precise and smooth linear motion.
Compared to traditional slide systems, linear guides—such as aluminium linear guide rail configurations—offer significantly higher load capacities, stiffness, and accuracy. Their rolling contact minimizes friction, resulting in faster motion capabilities and extended component life. They can support loads in both horizontal and vertical orientations while maintaining stable performance under dynamic conditions like rapid acceleration or deceleration.
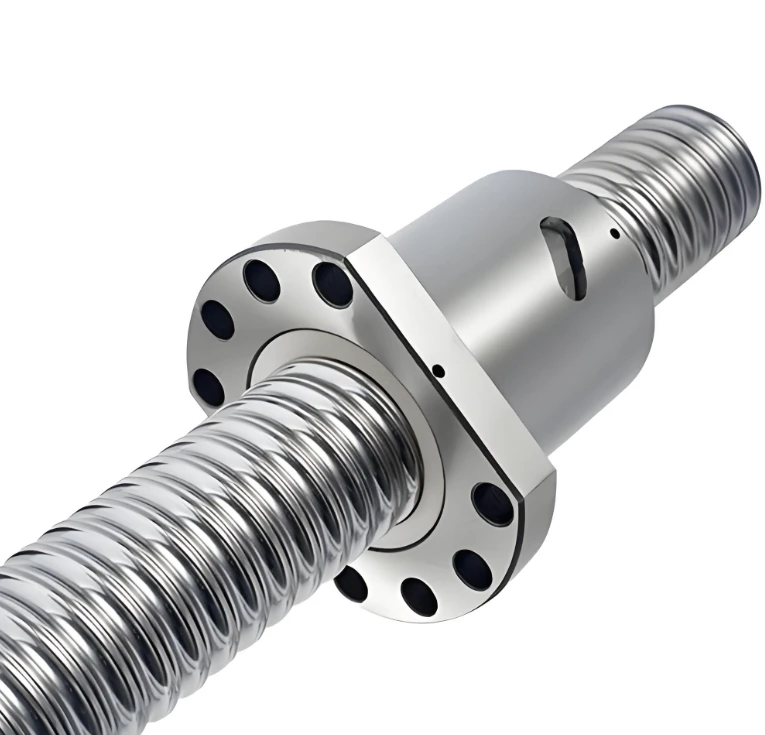
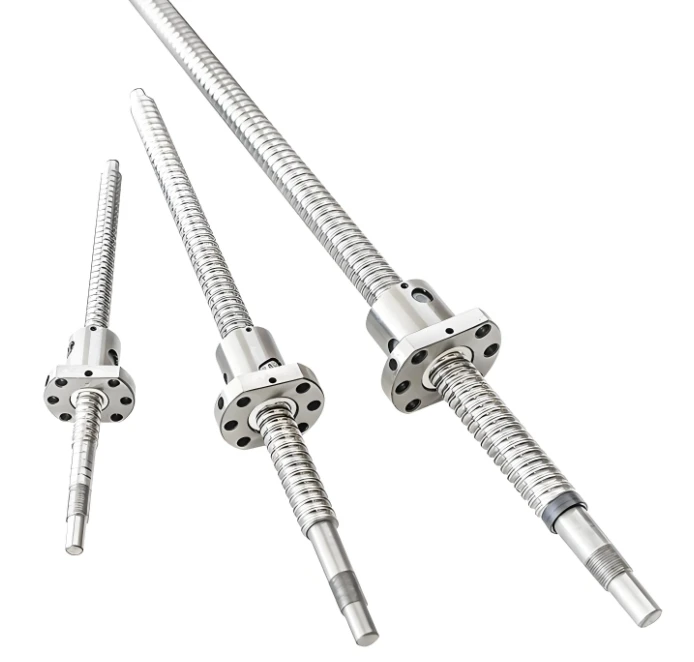
Linear guides are offered in various sizes, preload settings, and precision classes to meet different design needs. Some applications benefit from ball screw and linear guide integration, especially where synchronized multi-axis movement is essential. Common types include ball-type, roller-type, and miniature guides. Materials typically include hardened alloy steel or stainless steel that has been precision-ground for added durability and corrosion resistance.
Thanks to their modular design, these components are simple to install, align, and maintain. Many models support self-lubrication and include dustproof seals, ensuring long-term reliability with minimal upkeep.
Whether in robotics, machine tools, semiconductor systems, or medical devices, linear guides—including models like linear guide for sale—consistently deliver the precision, efficiency, and stability that modern automation systems demand.