Durable Ball and Roller Bearings for Heavy Load and Precision Applications
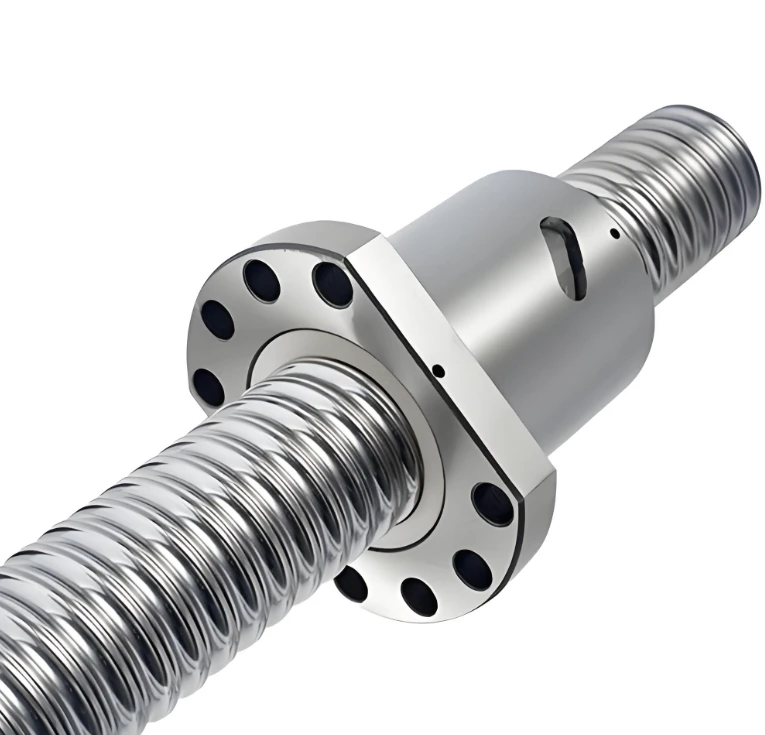
A bearing is a critical mechanical component designed to support and guide rotating or sliding shafts, reducing friction between moving parts and enabling smooth motion. Bearings are essential in virtually every type of machinery, from automotive engines and electric motors to industrial equipment and household appliances.
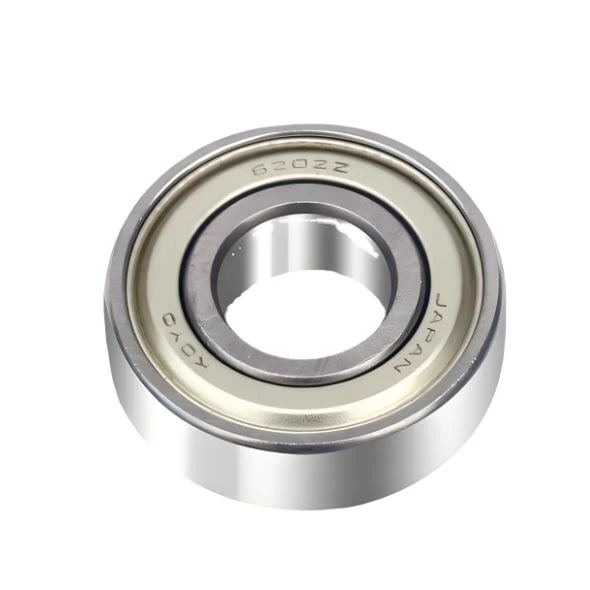
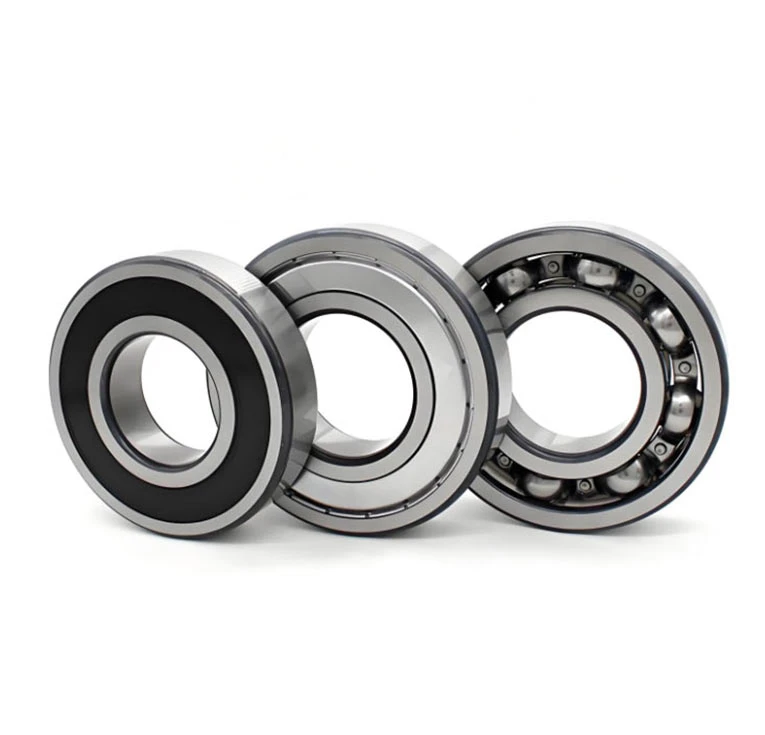
There are various types of bearings tailored to different applications, including ball bearings, roller bearings, tapered roller bearings, needle bearings, and thrust bearings. Among these, ball bearings are widely used due to their versatility, supporting both radial and axial loads with low friction. Roller bearings excel in handling heavy radial loads, while tapered roller bearings are optimized for combined radial and axial loads.
Bearings are manufactured from high-quality materials such as chrome steel, stainless steel, and ceramic, often with specialized heat treatments and surface finishes to enhance durability, corrosion resistance, and performance. Precision machining and grinding ensure tight tolerances, low noise, and long service life.Key performance factors for bearings include load capacity, speed rating, friction coefficient, and operating temperature range. Proper lubrication—whether grease or oil—is critical to minimize wear and prevent premature failure.
With advancements in materials and design, modern bearings offer high reliability even in harsh environments, such as high temperatures, heavy loads, or exposure to contaminants. Sealed or shielded bearings provide protection against dust and moisture, reducing maintenance needs.